Ever wondered whether you should say “a quicker route” or “a faster route”? You’re not alone. Many English speakers—native and learners alike—confuse “quicker” and “faster.” Both words talk about speed, but they don’t mean the same thing in every situation.
Understanding when to use each can sharpen your writing, make your speech more natural, and help you sound more fluent. Let’s break it down clearly and practically.
Why “Quicker” vs. “Faster” Confuses So Many People
At first glance, quick and fast seem interchangeable. Both describe something happening with little delay. But the truth lies in how and where they apply.
The confusion stems from overlap. You can take a faster train, but also a quicker path. You can finish quicker than expected, but run faster than your friend.
So, what’s really the difference? In essence:
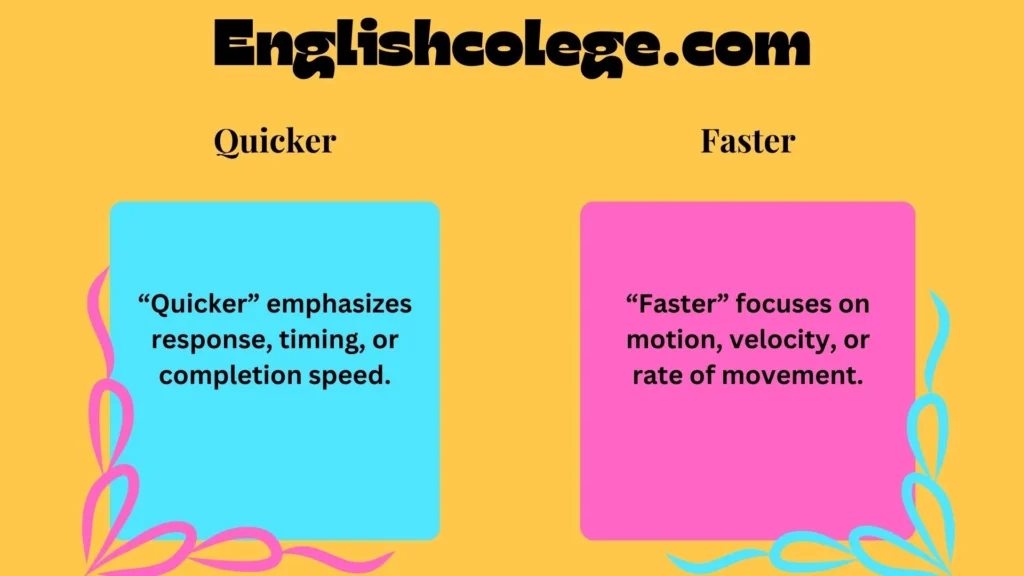
- “Quicker” emphasizes response, timing, or completion speed.
- “Faster” focuses on motion, velocity, or rate of movement.
Let’s explore that distinction deeper.
⚖️ The Core Difference at a Glance
Here’s a quick breakdown of “quicker” vs. “faster” for easy understanding:
| Feature | Quicker | Faster |
|---|---|---|
| Core Meaning | Reacting, responding, or completing sooner | Moving or operating at higher speed |
| Associated With | Time, decision-making, processes | Movement, vehicles, performance |
| Example | “She gave a quicker answer.” | “He ran faster than me.” |
| Grammar Form | Comparative of quick (adjective/adverb) | Comparative of fast (adjective/adverb) |
| Used For | Efficiency and reaction | Speed and rate |
| Focus | Timeliness | Velocity |
Think of it this way:
“Quick” is about how soon, while “fast” is about how much speed.
⏱️ What “Quicker” Really Means
Definition and Core Idea
“Quicker” means something happens with less delay or sooner than expected. It implies reaction time or completion efficiency, not necessarily physical speed.
Everyday Usage
You often use quicker when referring to mental actions, decisions, or processes rather than physical motion.
For example:
- “She responded quicker this time.”
- “We took a quicker route to avoid traffic.”
- “The quicker you start, the better the result.”
In these examples, “quicker” focuses on how soon something happens, not how fast something moves.
Contextual Examples
| Situation | Correct Usage | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Completing a task | “He finished the project quicker than last year.” | Focus on completion time |
| Reaction or decision | “She thought of the answer quicker.” | Focus on mental reaction |
| Communication | “Reply quicker next time.” | Emphasis on responsiveness |
Grammar Tip
“Quicker” is the comparative form of quick.
It can be used as both an adjective (“a quicker method”) and an adverb (“work quicker”).
💡 Note: In formal writing, “more quickly” can replace “quicker.”
Example: “He reacted more quickly” = “He reacted quicker.”
🚀 What “Faster” Really Means
Definition and Core Idea
“Faster” describes speed or velocity — how quickly something moves, performs, or operates. It’s often used for physical or measurable speed.
Everyday Usage
You use faster when referring to motion, machinery, vehicles, or performance rates.
Examples:
- “The car is faster than before.”
- “She runs faster than her brother.”
- “This computer runs faster after the upgrade.”
Contextual Examples
| Situation | Correct Usage | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Movement | “He ran faster than anyone.” | Refers to physical motion |
| Machine speed | “This fan spins faster.” | Rate of mechanical movement |
| Performance | “Faster delivery saves time.” | Speed of action or system |
Grammar Tip
“Faster” is both the comparative form and adverb form of fast.
It’s commonly used for measurable speed or physical motion.
💬 Comparative Examples: “Quicker” vs. “Faster” in Sentences
To see them in action, let’s compare side-by-side examples:
| Context | Sentence Using “Quicker” | Sentence Using “Faster” | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Replying | “He replied quicker this time.” | ❌ “He replied faster this time.” | “Reply” is a mental/response action. |
| Movement | ❌ “He walked quicker.” | “He walked faster.” | “Walk” involves motion. |
| Task Completion | “A quicker route saved time.” | “A faster route saved time.” | Both may work, but “quicker” implies efficiency. |
| Machines | ❌ “A quicker car.” | “A faster car.” | Cars are measured by speed, not timing. |
| Service | “Quicker service improves satisfaction.” | “Faster service improves turnaround.” | Both can work — depends on focus. |
👉 Rule of Thumb:
If it’s about reaction or efficiency, use quicker.
If it’s about speed or movement, use faster.
🧭 Context Matters: How to Choose the Right Word
The right choice depends on what’s being described.
1. Mental vs. Physical Actions
- Mental or process-related → use quicker
Example: “She came up with an idea quicker than anyone.” - Physical or measurable motion → use faster
Example: “He drives faster on highways.”
2. Processes vs. Performance
- Process or workflow improvement → “quicker”
Example: “A quicker way to register online.” - Machine or performance enhancement → “faster”
Example: “A faster processor improves performance.”
3. Informal vs. Technical Use
- In technical contexts, “faster” is usually correct (e.g., internet speed).
- In conversational English, “quicker” often feels more natural for everyday actions.
Visual Diagram:
[Mental/Process] → Quicker → Efficiency / Timing
↓
[Physical/Performance] → Faster → Speed / Velocity
⚠️ Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Mistake 1: Using “faster” for reactions
❌ “He replied faster.”
✅ “He replied quicker.”
Why? Because replying involves thought, not motion.
Mistake 2: Using “quicker” for machines
❌ “A quicker engine.”
✅ “A faster engine.”
Why? Machines have measurable speed, not reaction time.
Mistake 3: Mixing both in one sentence unnecessarily
Avoid: “He took a faster and quicker path.”
Pick one based on the meaning.
🌍 Real-World Scenarios and Examples
In Business
- “A quicker response to customer inquiries improves satisfaction.”
- “A faster internet connection boosts productivity.”
In Sports
- “He reacted quicker to the serve.”
- “She ran faster in the final lap.”
In Technology
- “This phone loads apps quicker after the update.”
- “This processor runs faster than the previous one.”
Case Study: Customer Support
Company A: Trained agents to reply quicker to emails.
Company B: Invested in faster servers to reduce lag.
Result: Both improved user satisfaction, but for different reasons — A improved response time, B improved system speed.
📈 Usage Trends and Data
Even though “faster” is slightly more common overall, “quicker” is trending in contexts like communication, business processes, and software efficiency.
According to corpus studies:
- “Faster” dominates in technical and physical contexts (transport, devices, speed).
- “Quicker” appears more in interpersonal and procedural contexts (responses, fixes, setups).
In modern English, both words are evolving:
“Quicker” now implies agility and efficiency, not just haste.
“Faster” continues to imply performance and measurable velocity.
🧠 Tips to Remember the Difference
Simple Mnemonic
“Quick = Response”
“Fast = Motion”
Memory Tricks
- If you can measure it → use faster.
- If you can react to it → use quicker.
- If it involves technology or vehicles → faster.
- If it involves thinking or responding → quicker.
Quick Practice Sentences
Try filling in the blanks:
- The internet is now _______ (quicker/faster).
- She replied _______ than before.
- The new train is _______ than the old one.
- A _______ way to solve the problem is using AI.
✅ Answers: 1. faster 2. quicker 3. faster 4. quicker
🔁 Related Comparisons You Might Find Helpful
- Speedy vs. Quick: “Speedy” emphasizes swiftness in action or movement, while “quick” can include thought and reaction.
- Rapid vs. Fast: “Rapid” often appears in scientific or formal contexts.
- Prompt vs. Quick: “Prompt” adds a sense of timeliness or readiness rather than mere speed.
❓ FAQs About “Quicker” vs. “Faster”
What’s the main difference between “quicker” and “faster”?
“Quicker” emphasizes reaction or timing; “faster” emphasizes motion or velocity.
Can I use “quicker” instead of “faster”?
Sometimes. If you’re referring to a process or response (not movement), yes. Otherwise, use “faster.”
Which is more formal: quicker or faster?
“Faster” tends to sound more technical or formal, while “quicker” is more conversational.
Is “more quick” correct?
Grammatically, yes, but it sounds awkward. Use “quicker” or “more quickly” instead.
Can both be used for time expressions?
Yes, but with nuance:
- “Quicker” = sooner or more immediate.
- “Faster” = shorter duration or higher speed.
🏁 Final Takeaway
Both “quicker” and “faster” express speed, but context defines which one fits best.
- Use quicker when describing how soon something happens.
- Use faster when describing how much speed something has.

I’m Sameer — a passionate English enthusiast who loves exploring words, grammar, and the art of effective communication. ✍️

